Archives
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
An alternative more rarely used electron microscopy based ap
2025-02-14
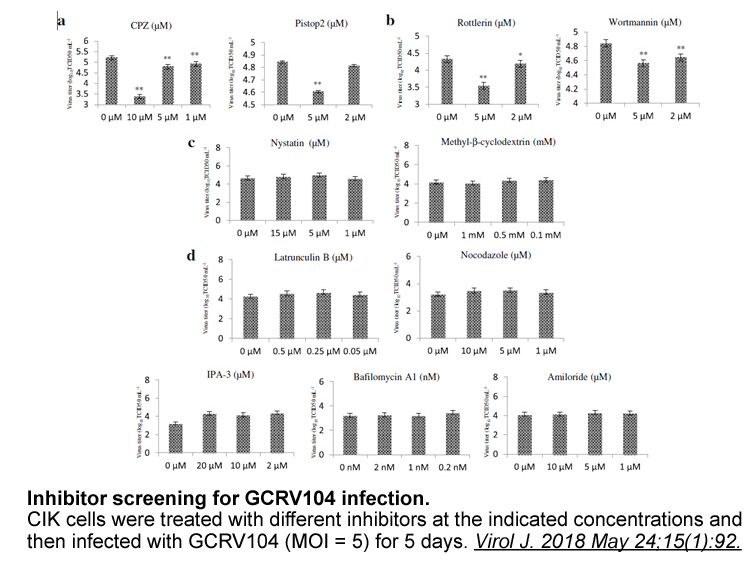
An alternative, more rarely used, electron microscopy-based approach exploits labeling of phagosomes with DAMP (3-(2,4-dinitroanilino)-30-amino-N-methyldipropylamine). DAMP is a weakly basic compound which is membrane-impermeable once it has been protonated. This way, DAMPH+ accumulates in acidic in
-
br ACL A Metabolic Checkpoint
2025-02-14
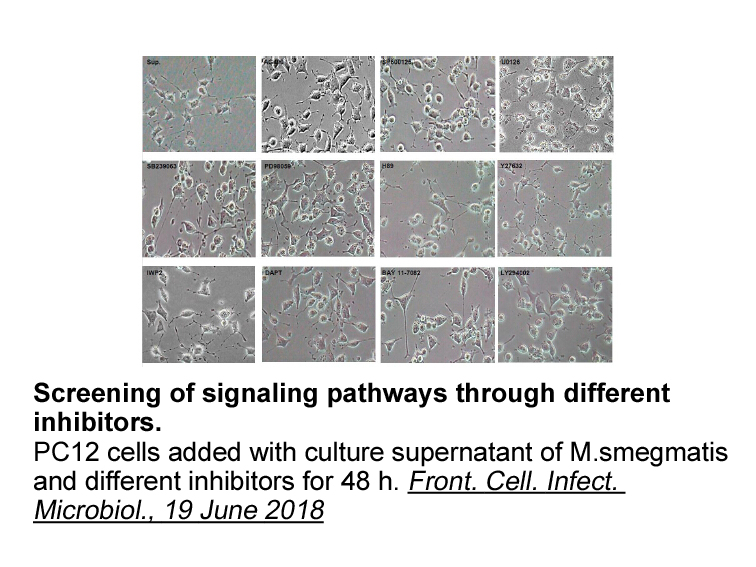
ACL: A Metabolic Checkpoint for Sensing Excess Nutrients? During normal transitions between fasting and feeding, cells maintain energy homeostasis by integrating energy and nutrient status signals at key metabolic nodes, coordinating multiple processes. For example, the AMP-activated protein kina
-
In addition to drawing attention to Ser of ACL
2025-02-14
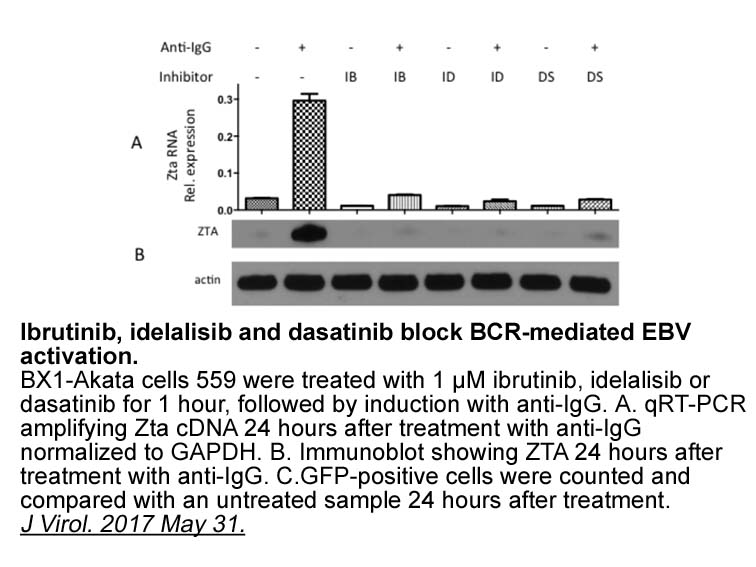
In addition to drawing attention to Ser454 of ACL as a phosphosite that is regulated by both BDK and PPM1K, our phospho-proteomics screen identified several additional sites in other proteins. For example, Ser25, Ser29, and Ser79 of the lipogenic enzyme acetyl-coA carboxylase 1 (ACC1) were found to
-
We next sought to determine the kinase responsible for
2025-02-14
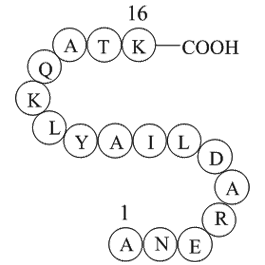
We next sought to determine the kinase responsible for IR-induced phosphorylation of 53BP1. Because the sites under investigation all lie in a consensus sequence for ATM, ATR and DNA-PK, that are all activated by IR, the involvement of each of these kinases was investigated. Preincubation of glut1
-
br Metabolic effects of apelin in obesity and type diabetes
2025-02-14
Metabolic effects of apelin in obesity and type 2 diabetes Mice fed a high fat diet (HFD) for several weeks become obese, hyperglycemic, hyperinsulinemic and insulin resistant. Acute apelin treatment by intravenous injection or by infusion during a hyperinsulinemic–euglycemic clamp in obese and i
-
cki mg br Results br Discussion Control of chronic
2025-02-14
Results Discussion Control of chronic inflammation is important in several inflammatory conditions like asthma, rheumatoid arthritis and fibrosis in lung diseases. The regulatory pathways that control chronic inflammation are complex and multi-factorial. Over expression of inflammatory mediato
-
Abnormalities in placentation in patients with
2025-02-14
Abnormalities in placentation in patients with PE appear to be associated with changes in different components of the signaling pathway that mediates cytotrophoblast migration/invasion. Studies have showed that the activation of the Notch signaling pathway is associated with the differentiation and
-
AR is expressed in cell
2025-02-14
AR is expressed in cell-specific human ovarian follicles at all stages of follicular development [25]. Administration of androgens in animals demonstrated initiation of follicular recruitment, stimulation of early stages of follicular growth, and increase in the number of growing follicles [26,27].
-
br HIF HIF signaling in
2025-02-13
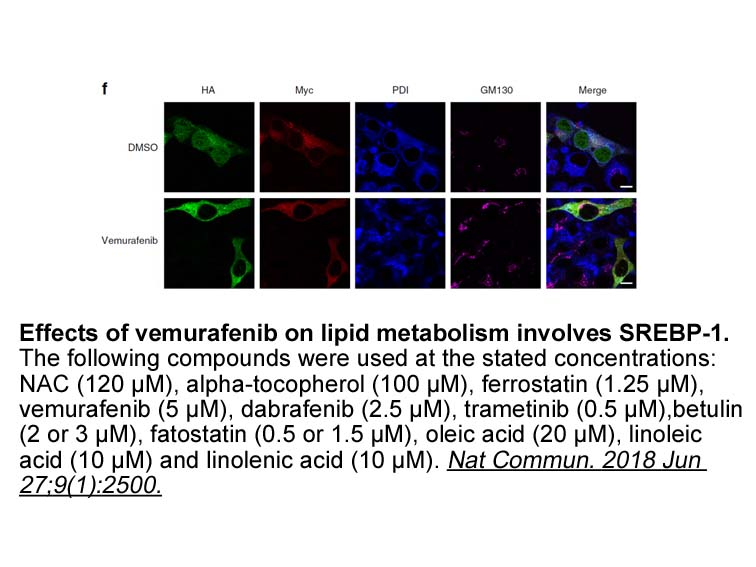
HIF-1α HIF-1α signaling in cancer cells contributes to tumor progression by promoting angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis, and the recruitment of immunosuppressive cells via secreted modulators 36, 37. One example of a HIF-1α immunosuppressive pathway is through increased expression of inducible n
-
The ARHL locus ahl that contributes to the hearing
2025-02-13
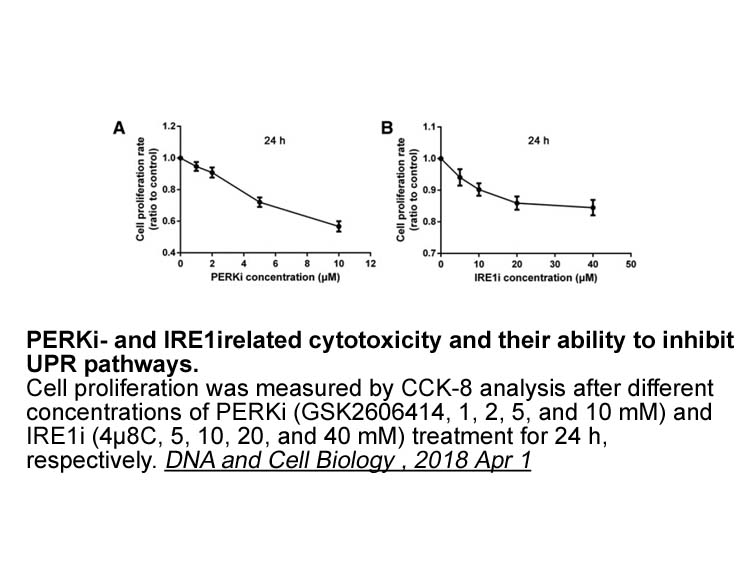
The ARHL locus (ahl) that contributes to the hearing loss in the C57BL/6J mouse has been mapped to chromosome 10 (Erway et al., 1993, Johnson et al., 1997). It has been shown that strains susceptible to early onset ARHL carry a specific mutation in the cadherin 23 gene (Cdh23), which encodes a compo
-
To reconstruct the amino acid sequence of
2025-02-13
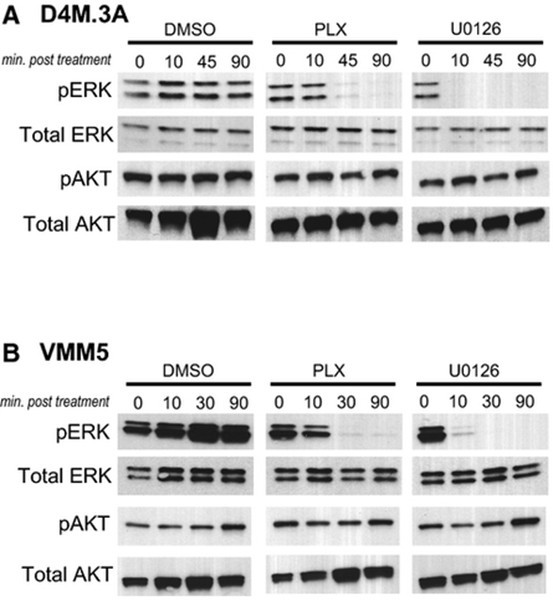
To reconstruct the amino Colistin Sulfate sequence of an ancestral β subunit a molecular phylogeny is required, which is inferred from a β subunit sequence alignment. To build this alignment we searched the NCBI database for proteins similar in sequence to the human muscle-type β subunit precursor
-
br Introduction Nausea and vomiting are
2025-02-13
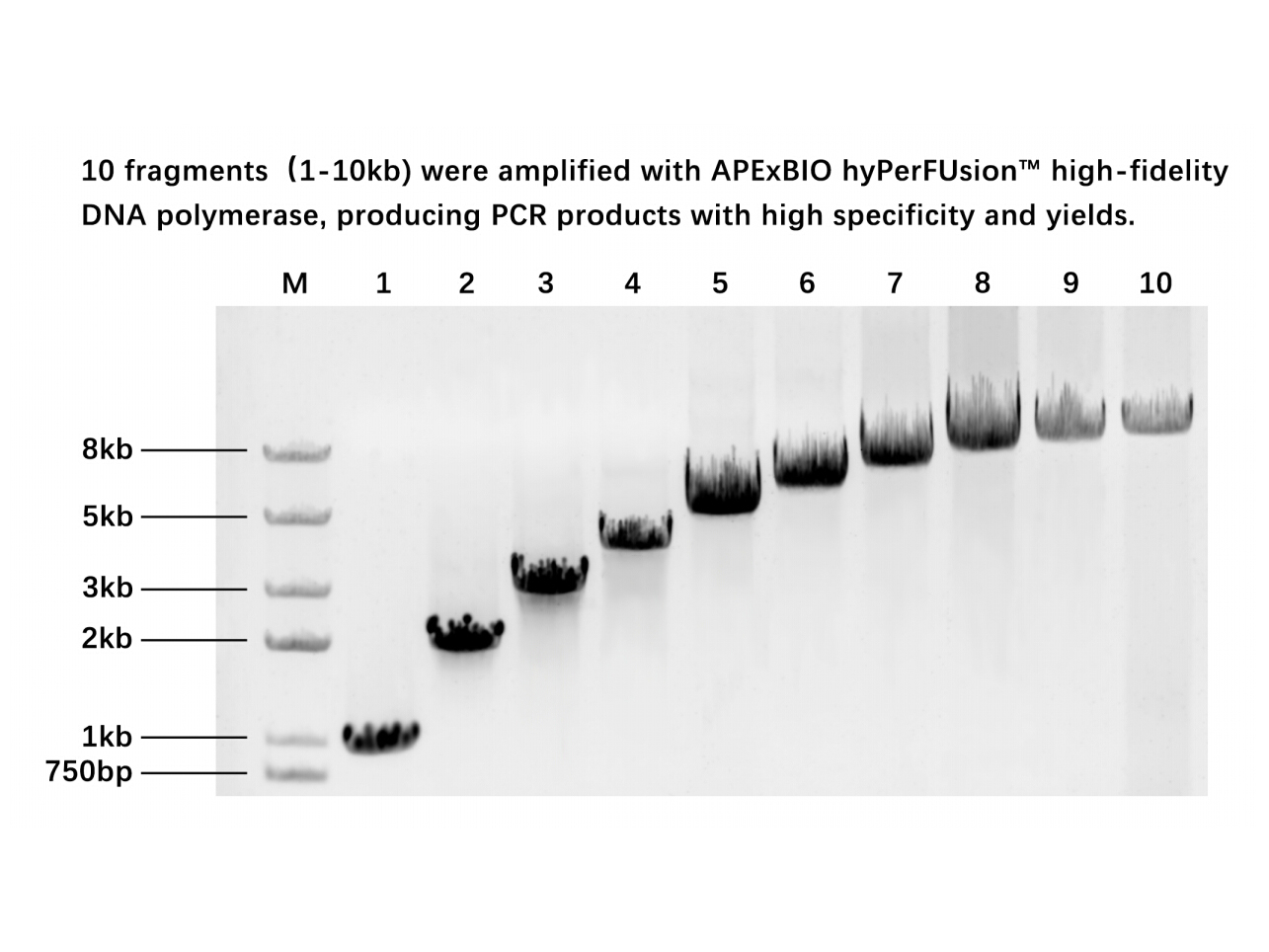
Introduction Nausea and vomiting are among the most distressing side effects associated with chemotherapy in cancer patients (Billio et al., 2010). Severe emesis can negatively affect a patient's nutritional state, ability to work and motivation, which can, in turn, interfere with the clinical co
-
The reductase family is composed
2025-02-13
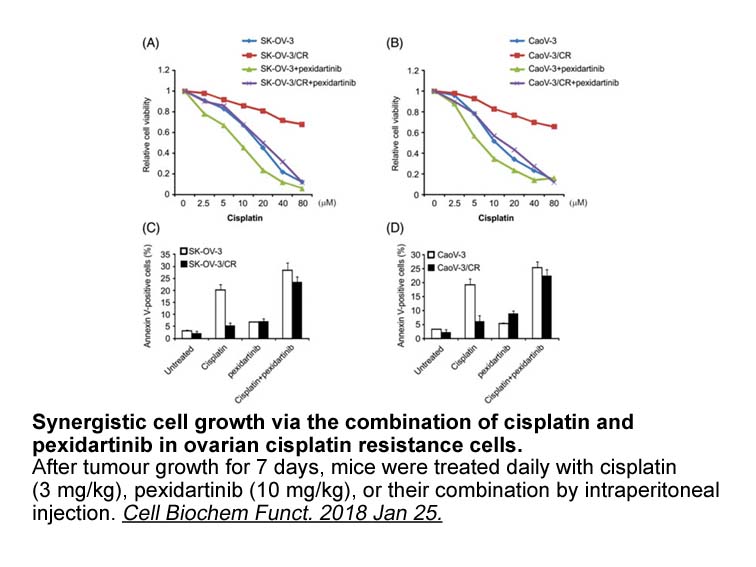
The 5α-reductase family is composed of three known isozymes, with the types I and II being the most known. Type I isozyme, which is the dominant form, can be found in the skin, liver, kidney, brain and lung. Furthermore, it has been evidenced that type I activity is several times higher in PC than i
-
br Concluding Remarks and Future Directions The physiologica
2025-02-13
Concluding Remarks and Future Directions The physiological significance of autophagy in neuronal function is steadily emerging. The studies discussed herein reveal that key neuronal functions, such as neurotransmitter release, pruning of dendritic spines, and behavioural outputs of neural network
-
If the lack of specificity and the high pleiotropy may
2025-02-13
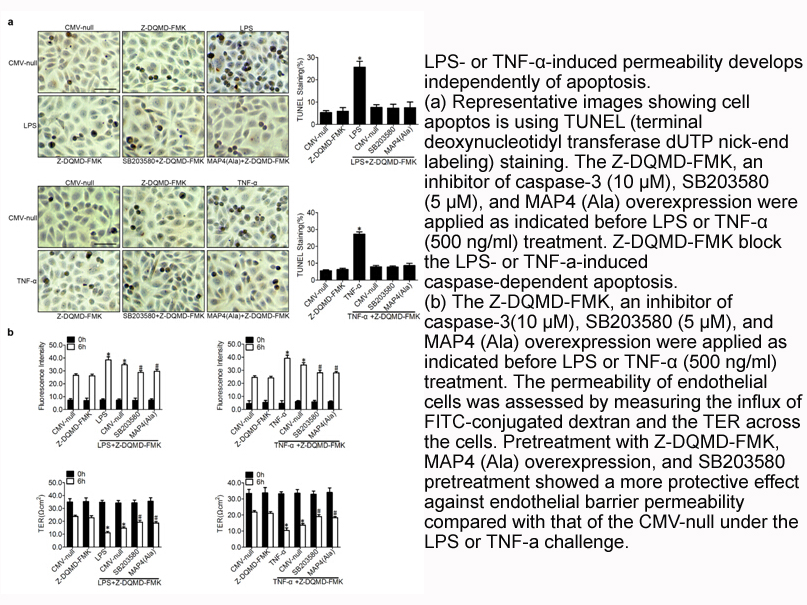
If the lack of specificity and the high pleiotropy may represent a problem in view of the potential chemotherapeutic features of autophagy-inducing agents, it Mefloquine hydrochloride may switch into an advantage in the case of chemopreventive strategies. In fact, as non-pharmacologic interventions
15496 records 16/1034 page Previous Next First page 上5页 1617181920 下5页 Last page